Business Analyst
The product strategy forms the basis for executing a product roadmap and subsequent product releases. The product strategy enables the company to focus on a specific target market and feature set, instead of trying to be everything to everyone.
When defining your product strategy be sure to answer the following questions.
Who are you selling to?
Define your target customer or market. Identify whom you are selling to, and what that market looks like.
What are you selling?
how potential customers will perceive your product compared to competitive products. Understand what makes your product unique in the market.
What value do you provide your customers?
Determine what problems your product solves for customers. You cannot be everything to everyone within a particular market, but you can help to solve specific problems. Create a value proposition to position the value you provide and the benefits that customers will receive with your solution.
How will you price your product?
State how you will price the product. Include its perceived value and a pricing model.
How will you distribute your product?
how you will sell your product, and how your target market will acquire your product.
Who are you selling to?
Define your target customer or market. Identify whom you are selling to, and what that market looks like.
What are you selling?
how potential customers will perceive your product compared to competitive products. Understand what makes your product unique in the market.
What value do you provide your customers?
Determine what problems your product solves for customers. You cannot be everything to everyone within a particular market, but you can help to solve specific problems. Create a value proposition to position the value you provide and the benefits that customers will receive with your solution.
How will you price your product?
State how you will price the product. Include its perceived value and a pricing model.
How will you distribute your product?
how you will sell your product, and how your target market will acquire your product.
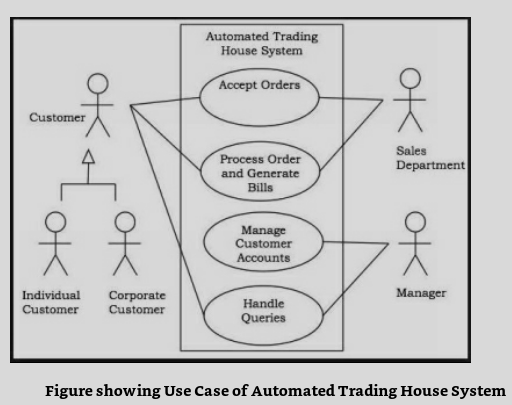
A use case is a list of actions or event steps, typically defining the interactions between a role (known in the Unified Modeling Language as an actor) and a system, to achieve a goal. The actor can be a human or a system.
Data is simply facts, figures, numbers, etc. It is the raw material that is processed to get some meaningful information. When data are processed, interpreted, organized, structured, or presented so as to make them meaningful or useful, they are called information.
E.g. the Test Score of each student is data. The average score of the whole class is information.
E.g. the Test Score of each student is data. The average score of the whole class is information.
Big Data as the name suggests is a large chunk of data with millions of rows and multiple columns. These are different from normal data because the data is so large that traditional data processing applications are inadequate.
Big data is a term that describes the large volume of data – both structured and unstructured – that inundates a business on a day-to-day basis. But it's not the amount of data that's important. It's what organizations do with the data that matters.
Big data is a term that describes the large volume of data – both structured and unstructured – that inundates a business on a day-to-day basis. But it's not the amount of data that's important. It's what organizations do with the data that matters.
*/?>
*/?>
*/?>
*/?>