Quantitative Methods - Quantitative Methods Section 2
- Option : B
- Explanation : When a dice is rolled, since there are a finite number of outcomes, it is an example of a discrete probability distribution. The continuous uniform distribution is defined over a range from a lower limit ‘a’ to an upper limit ‘b’. A normal distribution is symmetrical and bell-shaped.
72. The notation "F (x) = P (X < x)" best describes which of the following?
- Option : A
- Explanation : The cumulative distribution function gives the probability that a random variable X is less than or equal to a particular value x, P (X < x). Probability function specifies probability that random variable takes on a specific value. Probability density function is used for continuous random variables.
- Option : B
- Explanation : Consider the tree diagram below: The probability of a price decrease is equal to the probability of a price change times the probability of a decrease given a change = 0.6 * 0.6 = 0.36.
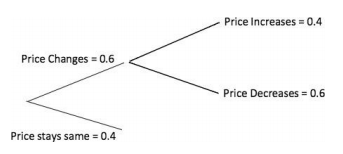 The probability of a price decrease is equal to the probability of a price change times the probability of a decrease given a change = 0.6 * 0.6 = 0.36.
The probability of a price decrease is equal to the probability of a price change times the probability of a decrease given a change = 0.6 * 0.6 = 0.36.
| Fund A | Fund B | ||
| Portfolio weights (%) | 45 | 55 | |
| Expected returns (%) | 23 | 13 | |
| Standard deviations (%) | 14 | 6 | |
| Correlation between the returns of Fund X and Fund Y | 0.7 | ||
The portfolio standard deviation of the returns is closest to:
- Option : B
- Explanation : The portfolio standard deviation of the returns is calculated through
following formula:
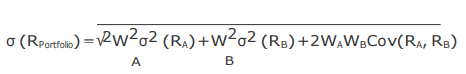 And covariance is calculated through following formula:
Cov(RARB)=ρ (RARB) σ (RA)σ(RB)
First calculate the covariance, Cov= 0.7 ∗ .14 ∗ .06 = 0.00588, then
enter values in the formula 1 for calculating portfolio standard
deviation, you should get portfolio standard deviation = 8.90%.
And covariance is calculated through following formula:
Cov(RARB)=ρ (RARB) σ (RA)σ(RB)
First calculate the covariance, Cov= 0.7 ∗ .14 ∗ .06 = 0.00588, then
enter values in the formula 1 for calculating portfolio standard
deviation, you should get portfolio standard deviation = 8.90%.
*/?>
*/?>
*/?>
*/?>


